Shogun: Total War is focused on samurai warfare in the Sengoku period of Japanese history, which lasted from the mid-15th century to the beginning of the 17th century. The game puts the player in the position of a Japanese daimyō with the objective of conquering Japan through military might, diplomacy, espionage, trade, and religion—thereby taking the position of shōgun. Shogun incorporates two main areas of play: The turn-based campaign map is where the player moves their armies, conducts diplomacy, builds the infrastructure of their provinces and performs various other tasks necessary to run their faction. The real-time element of the game allows the player to assume command of one of their armies and personally direct the course of any battles that take place.
The game consists of seven factions which the player can choose to play as each one of Japan's historical clans. The island of Kyūshū and the southwestern end of Honshū incorporates the Shimazu, Mōri and Takeda clans, while the Oda and Imagawa clans control the central parts of Honshū. The northern parts of Honshū are home to the Uesugi and Hōjō clans. While each clan has access to the same broad units and technology and begins the game with roughly the same amount of land, each clan has a specific advantage in a particular area. For instance, the Imagawa clan trains more efficient espionage agents, while the Takeda clan can produce higher quality cavalry, etc. Smaller, independent factions are represented as rebel clans and rōnin.
Campaign
The main campaign of Shogun: Total War involves a player choosing a clan and moving to eliminate their enemies and become shogun of feudal Japan. Each faction controls various historical provinces. Each province allows for the cultivation of farmland, and the construction of border watchtowers and a castle. Certain provinces possess natural resources that require a mine to be constructed to tap into. Coastal provinces may also construct ports to increase trade. Each castle has space to expand with a variety of military buildings and dojos, which allow for specific army units and agents to be produced. However, each castle can only support a certain number of auxiliary buildings. Castles can be upgraded to increase their defences and resilience to a siege. The production of units and construction of buildings is limited by the amount of koku the player has; koku is generated depending on the strength of the faction's economy and harvest. Units and buildings take time to produce; each turn represents one season.
During each turn, the player is able to move units about the map. Units come as either armies or agents and can only be moved to a province that borders the one in which they reside. However, both agents and armies can travel longer distances using ports, allowing them to move from one coastal province to another with a port in a single turn. Armies consist of military units such as spearmen, cavalry and archers. Should an army enter a battle, these units will be reproduced for the game's real-time tactics mode. Each army is led by a general that possesses an honour rating that rises and falls with the general's success or failure; if a general repeatedly endures defeat, they may commit seppuku. The faction daimyō and his heirs are also represented as generals—if a daimyō is killed and has no available heirs, the faction is eliminated from the game.
When an army is moved into an enemy or neutral province, it will engage in battle with whatever hostile armies already reside in the province. An army may also lay siege to a province's castle; after a determined amount of time, a castle's supplies will run out and the garrison will be forced to surrender if it does not break the siege or receive relief. A siege may cause damage to the castle's buildings, requiring repairs to be sought.
Several agents are available to each faction. The basic agent is the emissary, which can be used to negotiate alliances and ceasefires, as well as attempt to bribe enemy or neutral armies to join the player's faction. As factions build up their infrastructure, other agents become available, such as ninja and shinobi, the former assassinates enemy generals and agents, while the latter can spy on enemy provinces or perform counter-insurgency in home provinces. Each agent has an honour rating that determines how successful they may be at any particular mission. As the game progresses, the player will come into contact with European traders; first the Portuguese Jesuits, who will exchange arquebuses for money and the adoption of Catholicism by the clan, and later the Dutch, who will sell arquebuses without requiring a conversion. If a faction changes from Buddhism to Catholicism, it is given the ability to produce Jesuit priests, who in addition to acting as emissaries, convert the population, therefore making rebellions due to religion less likely.
Warfare
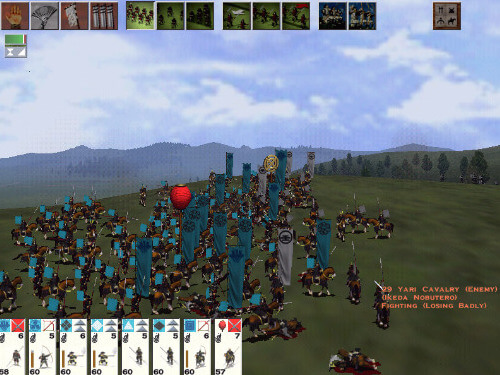
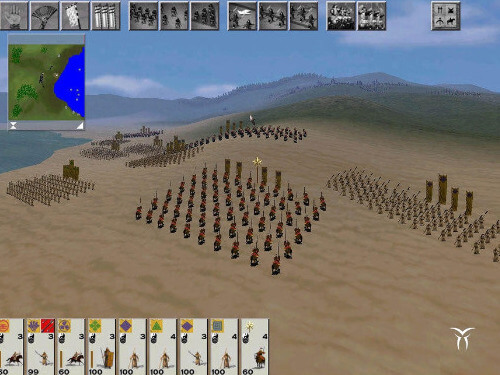
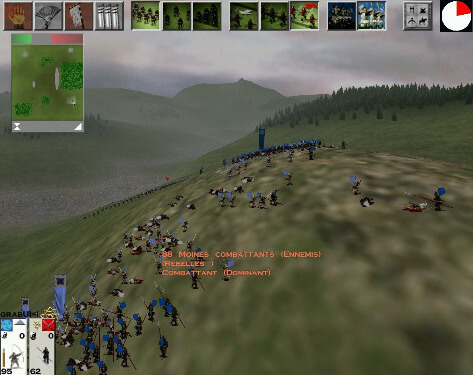
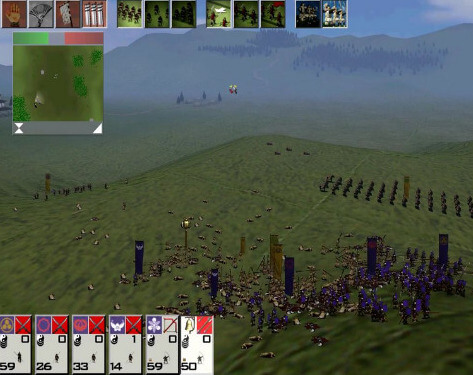
The battle system forms the second area of gameplay. Unlike the campaign part of the game, players control battles in real-time. However, should the player choose, the game can automatically resolve battles on the campaign map, taking into account factors such as the strength of numbers, the weapons used, and the terrain. Outside of the main campaign mode, players can participate in recreations of the historical battles that comprised the Sengoku period. In each battle, players are given access to an army consisting of a variety of units. Units come in the form of samurai and ashigaru, and fall into the categories of archers, spearmen, cavalry and heavy infantry. Each unit has its own intrinsic advantages, disadvantages, cost and overall level of effectiveness.
Players must use contemporary tactics and formations with the units they have available to defeat their enemies; the teachings of Sun Tzu's The Art of War are integral to the tactics used by the game's artificial intelligence and for the player to succeed. The terrain of the battlefield and the weather impact on how a battle is fought. Each unit has morale, which can increase if the battle goes well for their clan or decrease in cases such as heavy casualties or the death of the general. If a unit's morale is broken, they will rout; in certain circumstances, however, routing units may be rallied by the general. Victory in battle is achieved by causing every enemy unit to rout, or by killing the opposing army. Armies can lay siege to castles, replacing open land battles with close-quarters combat within the confines of the castle walls.