Final Fantasy XII is a fantasy role-playing video game developed and published by Square Enix for the PlayStation 2 home video console. A part of the Final Fantasy series, the game was released in 2006. It introduced several innovations to the series: an open world; a seamless battle system; a controllable camera; a customizable "gambit" system, which lets the player control the artificial intelligence (AI) of characters in battle; a "license" system, which determines what abilities and equipment can be used by characters; and a hunting side quest, which allows the player to find and defeat increasingly difficult monsters in the game's open world. Final Fantasy XII also includes elements from previous games in the series, such as Chocobos and Moogles.
The game takes place in the fictional land of Ivalice, where the empires of Archadia and Rozarria are waging an endless war. Dalmasca, a small kingdom, is caught between the warring nations. When Dalmasca is annexed by Archadia, its princess, Ashe, creates a resistance movement. During the struggle, she meets Vaan, a young adventurer who dreams of becoming a sky pirate in command of an airship. They are quickly joined by a band of allies; together, they rally against the tyranny of the Archadian Empire.
Final Fantasy XII received critical acclaim, earning numerous Game of the Year awards. As of November 2009, the game sold over six million copies worldwide on PlayStation 2. A sequel, Final Fantasy XII: Revenant Wings, was released for the Nintendo DS in 2007. A high-definition remaster of the International Zodiac Job System version, subtitled The Zodiac Age, was released for the PlayStation 4, Microsoft Windows, Nintendo Switch, and Xbox One.
Gameplay
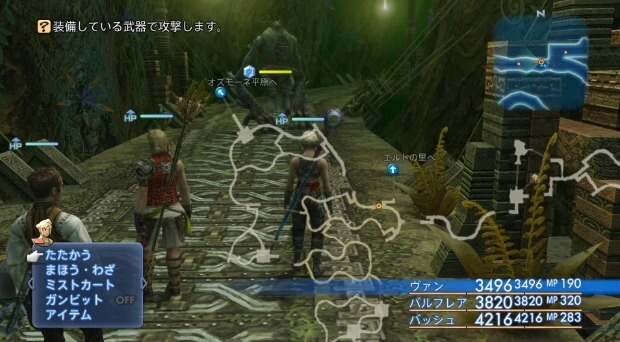
Throughout the game, the player directly controls the on-screen character from a third-person perspective to interact with people, objects, and enemies. Unlike previous games in the series, the player can also control the camera with the right analog stick, allowing for a 360° view of the surroundings. While in towns and cities, the player may only see from the perspective of Vaan, but any character may be controlled in the field. The world of Final Fantasy XII is rendered to scale relative to the characters in it; instead of a caricature of the character roaming around miniature terrain, as found in the earlier Final Fantasy games, every area is represented proportionally. The player navigates the overworld on foot, Chocobo, or by airship. Players may save their game to a memory card using save crystals or gate crystals, and may use the latter to teleport between gate crystals. An in-game bestiary provides incidental information about the world of Final Fantasy XII.
Final Fantasy XII restructures the system of earning gil, the currency of the Final Fantasy games; instead of gil, most enemies drop "loot" which can be sold at shops. This ties into a new battle mechanic which rewards the player with improved loot for slaying a particular type of enemy multiple times in a row. Selling different types of loot also unlocks a bazaar option in shops, which provides items at a lower cost, or items exclusive to the bazaar.
Battle system
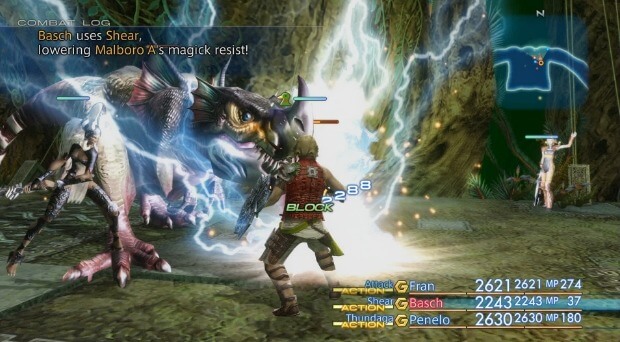
Excluding the massively multiplayer online role-playing game Final Fantasy XI, Final Fantasy XII is the first entry in the main Final Fantasy series not to include random encounters. Instead, enemies are visible in the overworld and the player may choose to fight or avoid them. Battles unfold in real time using the "Active Dimension Battle" (ADB) system. Battles begin when the party comes within range of an aggressive enemy, the party attacks an enemy, or a story event initiates a confrontation. When a character or enemy begins an action, target lines connect characters to other party members or enemies; different colors represent the different types of action. The player may swap to and issue commands to any of the three characters in the party, but guest characters are controlled by artificial intelligence (AI). Battle commands are initiated through a series of menus, and include Attack, Magicks, Technicks, Mist, Gambits, and Items. The player may switch any active character with an inactive character at any time, unless the active character is targeted by an attack or ability. Characters who are knocked out may also be substituted.
A new feature in Final Fantasy XII is the "gambit" system, which allows the player to program each character to perform certain commands in battle in response to specified conditions. Using gambits, the player may set reactions to different stimuli for each character. Each gambit consists of three parts: a target, an action, and a priority. The target specifies which ally or foe to act on and the condition for applying the action. For example, the target "Ally: HP < 70%" causes the character to target any ally whose hit points have fallen below 70%. The action is the command to be performed on the target. The priority determines which gambit to perform when multiple gambits are triggered. These heuristics guide the characters when acting autonomously, though player-directed commands are always given top priority.
In Final Fantasy XII, a mysterious phenomenon known as "Mist" is the key energy which allows characters to cast summoning magic and perform "Quickenings". After defeating an Esper in combat, the player will be able to summon it to the battlefield. Similar to Final Fantasy X, the summoned creatures become active participants in battle, as opposed to the cinematic attacks seen in previous games in the series. Unlike Final Fantasy X, however, Espers follow hidden gambits, rather than the player's direct command. The summoner remains an active member in the fight, able to attack and cast support magic, instead of leaving the party or standing idle while the summoned creature fights. An Esper will leave the battle if either the summoner or itself is knocked out, its time limit expires, or it executes its special attack. Some Espers have origins in Final Fantasy Tactics and Final Fantasy Tactics Advance and others are derived from the final bosses of previous Final Fantasy games such as Chaos, the final boss of the first Final Fantasy, and Zeromus, the final boss of Final Fantasy IV.
Final Fantasy XII introduces "Quickenings", a new Limit Break system unique compared to those in previous games in the series. Characters learn Quickenings by progressing to specific panels on the License Board. Each character can learn three Quickenings, which are unique to that character. Characters may string together Quickenings into large combo attacks, called Mist Chains, via timed button presses. If a Mist Chain reaches a certain length, a final strike will be initiated at the end of the Quickening cycle, called a Concurrence.
Growth system
As in many role-playing games (RPGs), characters "level up" each time they earn a set number of experience points from defeating enemies; each level gained increases the character's statistics and improves performance in battle. Statistics include hit points, the amount of damage a character can receive; strength, the power of the character's physical attacks; and magic, the potency of the character's magical spells.
In addition to leveling up, players may improve their characters via the License Board. The License Board is an array of panels that contain "licenses" which allow a character to perform certain actions. The board is split into two parts; the upper part comprises Magick, Technick, Accessory, and Augment (stat increases and other permanent buffs) licenses, and the bottom part comprises mostly Weapon and Armor licenses. To use a Magick, Technick, or piece of equipment, the character must obtain its corresponding license by spending the required amount of LP (License Points). LP are earned in battle along with the experience points. Like the Sphere Grid in Final Fantasy X, all characters may obtain all licenses on the board; however, each Quickening and Esper license may only be activated by a single character.